Exploring Routing Protocols In MikroTik RouterOS
If you're looking to optimize your network routing and management, you may have come across references to static routing in MikroTik. But what exactly is static routing, and how can it benefit your network? In this article, we'll explore the ins and outs of static routing in MikroTik, including:
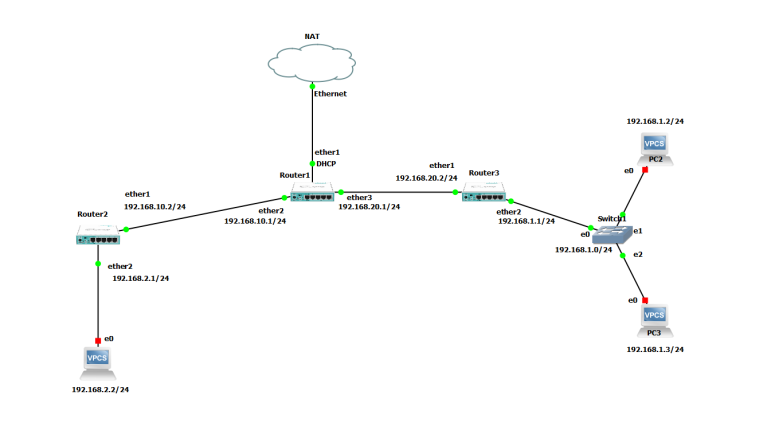 First and foremost, it's important to understand the difference between static and dynamic routing. Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIP, allow routers to exchange information about their networks and automatically determine the best path to a given destination. Static routing, on the other hand, involves manually configuring routers to specify the paths that traffic should take through the network.
First and foremost, it's important to understand the difference between static and dynamic routing. Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIP, allow routers to exchange information about their networks and automatically determine the best path to a given destination. Static routing, on the other hand, involves manually configuring routers to specify the paths that traffic should take through the network.
So, why might you choose static routing over dynamic routing? One advantage is that static routing can be simpler and more predictable, since you have complete control over the paths that traffic will take. This can be particularly useful in smaller networks or those with relatively stable traffic patterns.
Here are some specific benefits of using static routing in MikroTik:
Simplicity
As mentioned above, static routing can be a simpler approach than dynamic routing. With static routing, you don't need to worry about configuring or troubleshooting routing protocols, and you have more control over how traffic flows through the network.
Speed
Since static routes are manually configured, they can be faster to converge than dynamic routes. Convergence refers to the process of detecting and reacting to changes in the network, such as a link going down. With dynamic routing protocols, the time it takes for routers to converge can vary depending on factors such as the size of the network and the complexity of the routing protocol.
Stability
Static routes can also be more stable than dynamic routes, especially in networks with fluctuating or unreliable connectivity. With dynamic routing protocols, the routing tables can change frequently as new paths are discovered or old ones become unavailable. This can make it harder to predict how traffic will flow through the network, and can lead to congestion or other performance issues.
Control
One of the biggest advantages of static routing is that it gives you complete control over how traffic moves through the network. You can choose specific paths for traffic based on factors such as bandwidth, latency, and security requirements. This level of control can be particularly useful in situations where you need to ensure certain traffic flows take priority over others.
Security
Since static routes are manually configured, they can be more secure than dynamic routes. With dynamic routing protocols, there is always the risk of malicious actors forging routing messages or exploiting vulnerabilities in the protocol. Static routing, on the other hand, is less vulnerable to these kinds of attacks, since the routing tables are manually configured and not susceptible to automated manipulation.
Scaling
While static routing can be a great solution for smaller networks, it may not be practical or efficient for larger or more complex networks. In these situations, dynamic routing protocols may be a better choice, since they can be more scalable and adaptive to changes in the network. However, even in larger networks, there may be specific situations where static routes can be useful.
Configuring static routes in MikroTik
Now that we've explored the benefits of static routing, let's take a look at how to configure it in MikroTik. Here are the basic steps:
- Open the MikroTik web interface and navigate to the IP > Routes menu.
- Click the + icon to add a new route.
- In the "Dst. Address" field, specify the network you want to route traffic to.
- In the "Gateway" field, specify the IP address of the next hop router for this network.
- Optionally, you can also specify other parameters such as distance, scope, and target-scope.
- Click "Apply" to save the new route.
That's it! Once the new route is added, traffic will be routed according to the path you've specified. Of course, as with any network configuration, it's important to thoroughly test and verify your changes before deploying them in a production environment.
Conclusion
Static routing can be a powerful tool for optimizing and securing your network, especially in smaller or less complex environments. By taking advantage of the benefits of static routes in MikroTik, you can gain more control, stability, and predictability over your network traffic.
 However, it's important to remember that static routing is not a one-size-fits-all solution. In larger or more complex networks, dynamic routing protocols may be a better choice. Ultimately, the specific approach you choose will depend on a variety of factors such as network size, performance requirements, and security concerns.
However, it's important to remember that static routing is not a one-size-fits-all solution. In larger or more complex networks, dynamic routing protocols may be a better choice. Ultimately, the specific approach you choose will depend on a variety of factors such as network size, performance requirements, and security concerns.
Whether you're a network administrator, IT professional, or simply a curious enthusiast, understanding the pros and cons of static routing can help you build more efficient and secure networks. By staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices, you can stay ahead of the curve and ensure that your network is running at peak performance.




Post a Comment for "Exploring Routing Protocols In MikroTik RouterOS"