Advanced Routing Techniques MikroTik RouterOS Tips And Tricks
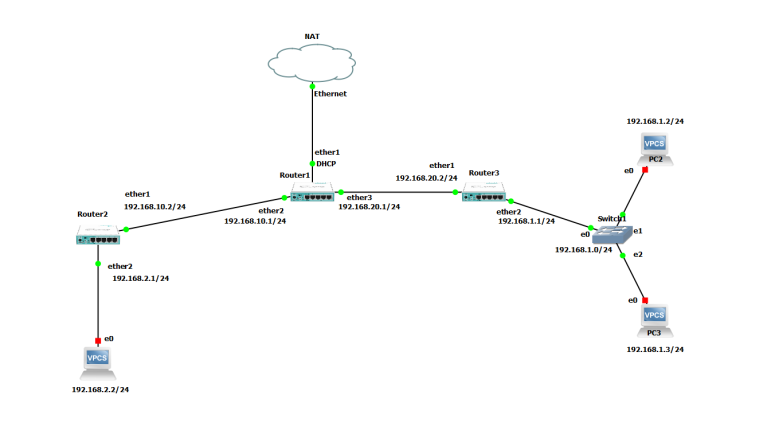
Have you heard of static routing? This technique is used to manually configure routing paths in a network. At its core, it involves manually configuring network routers and systems to map out precise routes that data packets can follow as they move between devices. If you're interested in getting a better understanding of static routing, then this article is for you!

What is Static Routing?
Static routing is a manual process that allows network administrators to manually configure paths to be taken by data packets as they move across a network. Essentially, static routing requires you to set up specific paths for your data to follow, rather than letting network devices figure out the best path to take on their own. This process can be time-consuming, but it can be useful in situations where you need to make sure that data packets are always taking the same path, especially if you need to prioritize certain types of data over others.
How Does It Work?
To understand static routing, you need to have a broad understanding of how networks operate. Normally, network devices, like routers, are capable of determining the best path to take for data packets as they move from one system to another. This routing happens automatically and instantly, thanks to protocols like the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Static routing, on the other hand, is done manually. Network administrators and engineers set up specific routes for data packets to take, specifying which devices and systems they should pass through before reaching their destination. Once these routes are established, they stay in place until they're manually changed or adjusted.
Advantages of Static Routing
Although static routing can be time-consuming, there are many benefits to using this technique. Some of the key advantages of static routing include:
- Simple Configuration: Static routing is simple to set up since it doesn't use complicated routing protocols. All you need to do is specify the path that packets should take between devices, and your network will start using this route.
- Guaranteed Path: When using static routing, you have complete control over the path that data packets take. This means that you can ensure that they always take the same route. This can be useful in situations where some paths may be slower or less secure than others.
- Low Resource Consumption: Because there's no need for complex routing protocols, devices that use static routing can use fewer resources. This means that they can be less expensive, and they're less likely to experience performance issues.
Disadvantages of Static Routing
Despite its many advantages, static routing does have some downsides. Some of the key disadvantages of static routing include:
- Inflexibility: Once you set up a static route, it stays in place until it's manually changed. This means that changes or adjustments must be made manually, which can be a time-consuming and difficult process.
- Inefficient Routing: With static routing, data packets always take the same path, even if other paths may be faster or more efficient. This can lead to slower network speeds and reduced performance.
- Not Scalable: As your network grows and changes, static routes become less and less useful. In large networks, it can be difficult to keep track of all the static routes that are in place, and making changes to these routes can be a difficult and time-consuming process.
When to Use Static Routing?
Static routing is useful in situations where you need to control the path that data packets take between devices. Some common use cases for static routing include:
- Connecting two networks together via a specific path
- Diverting traffic away from a congested network segment
- Routing traffic over a secure connection
- Prioritizing certain types of traffic over others
- Isolating specific devices or systems from other parts of the network
How to Configure Static Routing?
To configure static routing, you'll need to follow several steps:
- Identify the IP addresses of the devices you want to connect
- Configure the devices to use static routing
- Create static routing entries on each device, specifying the path that packets should take
- Test the connection between the devices to ensure that they're properly connected.
Conclusion
Static routing is a useful technique for controlling the path that data packets take across a network. While it can be time-consuming to set up, static routing offers complete control over the routing path, making it useful in situations where network performance needs to be optimized. That being said, static routing isn't always the best solution for all situations, and it should be used with care. If you're not sure whether static routing is right for your network needs, it's always a good idea to consult with an experienced network engineer.


Post a Comment for "Advanced Routing Techniques MikroTik RouterOS Tips And Tricks"